|
Affordable Care Act Reduces Racial
Disparities in Health Care Coverage
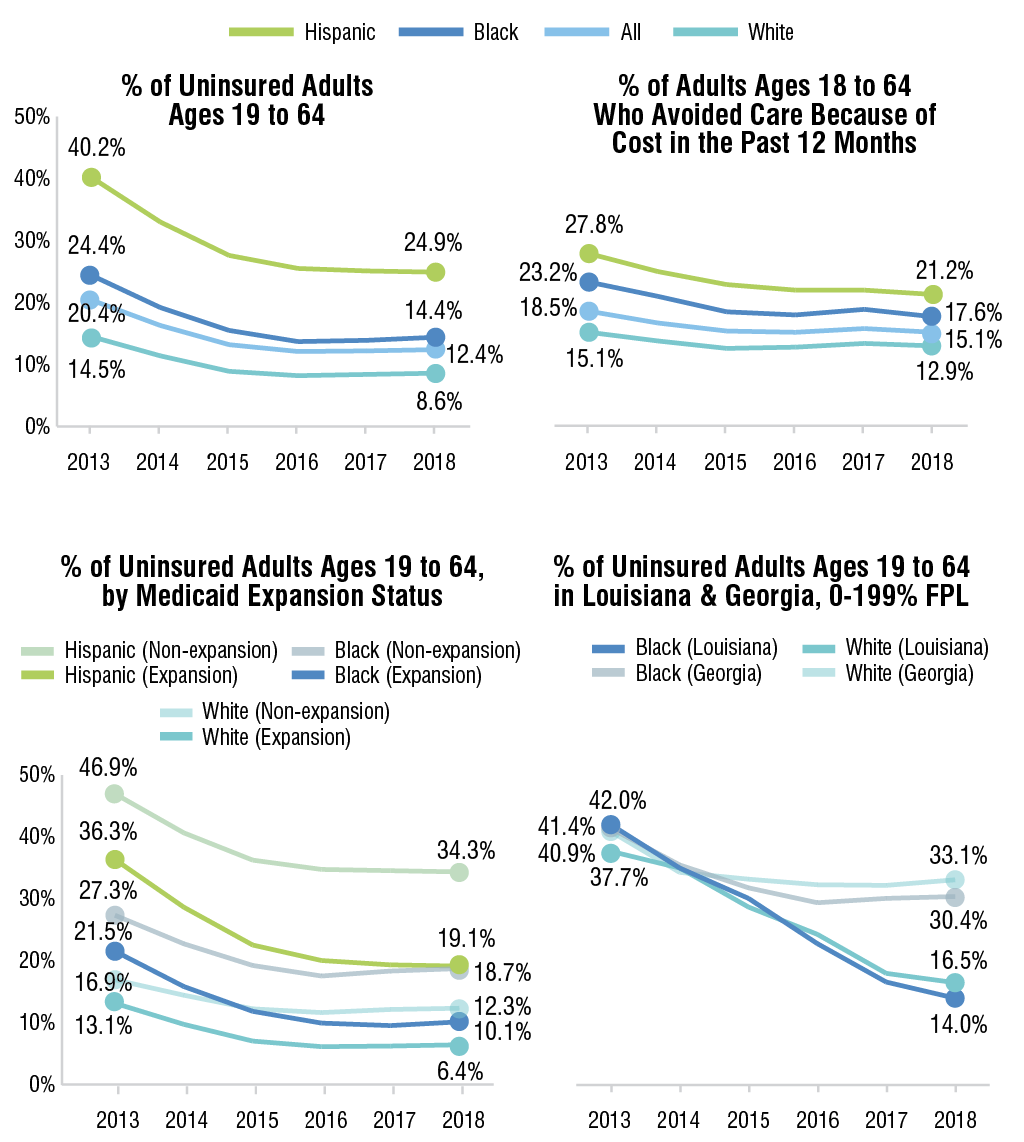
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has significantly reduced
racial disparities in access to health care since 2014, according to a
recent analysis by The Commonwealth Fund. The gap between uninsured rates
for black adults and white adults declined 4.1 percentage points, while the
gap between Hispanic and white adults dropped 9.4 points. All three racial
groups saw lower uninsured rates and larger coverage improvements in
Medicaid expansion states between 2013 and 2018. The report also compared
the uninsured rate changes in Louisiana, which expanded Medicaid in 2016,
and in Georgia, which did not expand the program. Both white and black
adults with incomes under 200% of the federal poverty level (FPL) saw
coverage improvements from 2013 to 2015 in both states. Yet while
Louisiana’s Medicaid expansion led to lower uninsured rates, Georgia’s
rates remained flat after 2016.
NOTES: Expansion states are those that expanded Medicaid by
Jan. 1, 2018. As of that date, there were 19 states that had not yet
expanded Medicaid. Maine and Virginia implemented Medicaid expansion in
2019 and are considered non-expansion for this analysis.
SOURCE: The Commonwealth Fund, "How the Affordable Care
Act Has Narrowed Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Access to Health
Care." Visit https://bit.ly/30MSQnR.
|

No comments:
Post a Comment